Code
A07
Year of Issue
none
Sector
Agriculture
The complete description of the NWRM
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| a7_-_low_till_agriculture.pdf | 954.35 KB |
Summary
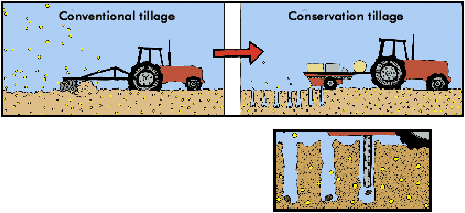
Low till agriculture, also known as conservation or reduced till applies to arable land. It consists of a combination of a crop harvest which leaves at least 30% of crop residue on the soil surface, during the critical soil erosion period and some surface work (low till). This slows water movement, which reduces the amount of soil erosion and potentially leads to greater infiltration.
Illustration(s)
 |  |
|
Benefit Table
Possible benefits with level
| Benefits | Level | |
|---|---|---|
|
BP7 - Increase soil water retention
|
Medium
|
|
|
BP10 - Reduce erosion and/or sediment delivery
|
Medium
|
|
|
BP11 - Improve soils
|
Medium
|
|
|
ES1 - Water storage
|
Low
|
|
|
ES5 - Climate change adaptation and mitigation
|
Low
|
|
|
ES6 - Groundwater/aquifer recharge
|
Medium
|
|
|
ES9 - Filtration of pollutants
|
Medium
|
|
|
ES10 - Recreational opportunities
|
Low
|
|
|
PO3 - Improving status of hydromorphology quality elements
|
Medium
|
|
|
PO7 - Prevent surface water status deterioration
|
Medium
|
|
|
PO9 - Take adequate and co-ordinated measures to reduce flood risks
|
Medium
|
|
|
PO11 - Better protection for ecosystems and more use of Green Infrastructure
|
High
|
|
|
PO12 - More sustainable agriculture and forestry
|
Low
|
|
|
PO14 - Prevention of biodiversity loss
|
Low
|